Definition of Measles Disease or Measles Virus or Measles Rash:
Measles disease is also known as rubeola which is a highly contagious infection that is caused by the measles virus. Measles is an airborne disease that spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of the infected one.
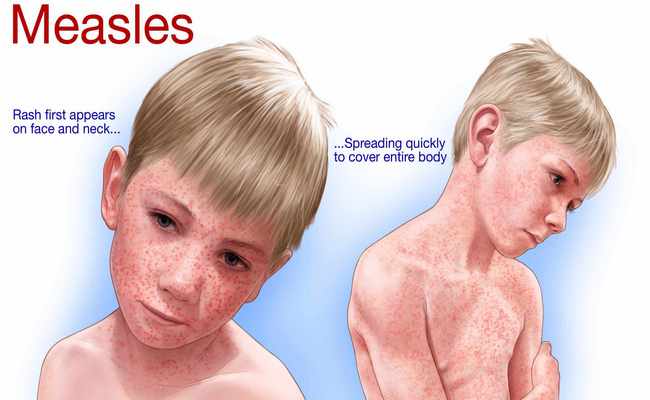
Symptoms of Measles Disease:
There are different type’s symptoms of measles; those are mentioned in the following:
- High fever,
- Malaise,
- Runny nose,
- Sneezing,
- Sore throat,
- Hacking cough,
- Red-eye and sensitivity to light (Conjunctivitis),
- Full body rash,
- Koplik’s spots (small red spots with blue-white centers that appear inside the mouth).
Different Periods for Measles Disease:
1.Incubation Period:
10-15days is the incubation period of Measles. On those days no signs or symptoms will appear.
2. Exposure Period:
The measles rash appears 2-4days after the initial symptoms and lasts for up to eight days. Measles typically begins with mild to moderate fever, accompanied by cough, runny nose sore throat, and red eyes. A small red rash first appears on to face then after few days spread to the whole body with 104°F to 105°F temperature.
3. Communicable Period:
Measles is infectious from starting four days before the rash appears and ending when the rash has been present for four days.
Risk Factors of Measles Disease:
Various risk factors for Measles are mentioned below:
1. Non immunized:
A person who did not receive the vaccine for measles.
2. International Travelers:
A person who travels from one country to another country may have a chance of measles.
3. Vitamin A deficiency:
A person who does not take sufficient vitamin-A-containing food, have more likely to be affected by measles and to have more chance for severe symptoms.
Causes of Measles Disease:
Measles disease is caused by a virus in the paramyxovirus family (A paramyxoviridae).
Mode of Transmission:
The measles virus is highly contagious. The measles virus is contained with the millions of tiny droplets that come out the nose and mouth when an infected person coughs or sneezes. So, measles is transmitted through droplets (Airborne) or direct contact with contaminated dust.
The virus remains active and contagious in the air or on infected surfaces for up to 2 hours. It can be transmitted by an infected person from 4 days before the onset of the rash to 4 days after the rash erupts.
Test and Diagnosis for Measles:
There are various types of test and diagnosis ways for measles disease; those are mentioned in the following:
- Clinical sign and symptoms,
- Physical examination,
- Blood test (IGM),
- Viral culture.
Treatment for Measles Disease:
No specific antiviral treatment exists for the measles virus but supportive treatment is necessary to relieve symptoms. There are different types of supportive treatment ways for Measles, those are mentioned below:
1. Control fever and relief pain:
Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen (Tylenol), or naproxen can reduce high fever and relief pain, ache.
2. Adequate rest and isolation:
Get plenty of rest and stay out of school, workplace, public place at least 4 days after the rash first appears.
3. Vitamin A supplements:
Two doses of vitamin A supplements should be taken 24 hours apart after exposure to Measles. Vitamin A helps to nourished children and can help to prevent eye damage and blindness.
4. ORS (Oral rehydration solution):
Ensure adequate fluid intake and to treat dehydration that is lost through diarrhea or vomiting.
5. Antibiotics:
Antibiotics should be prescribed to treat eye and ear infections and pneumonia.
Complications for Measles Disease:
There are different types of complications for measles, those are mentioned below:
- Ear infection (Otitis media),
- Bronchitis, Laryngitis,
- Diarrhea and vomiting,
- Pneumonia,
- Encephalitis,
- Pregnancy problems(Miscarriage or premature labor),
- Thrombocytopenia,
- Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE).
Prevention for Measles Disease:
Various types of prevention for measles are mentioned below:
- Isolation,
- Vaccination (MMR),
- Pregnant women should be vaccinated by HNIG injection.
Nursing Intervention for Measles Disease:
There are different types of nursing intervention for measles disease; those are mentioned in the following:
- Assess the patient for the severity of symptoms.
- Check the mouth for sore throat and koplik’s sign.
- Check the patient that he/she is eating well or not.
- Encourage the patient to take food adequately and assure food (Semisolid) as the patient likes.
- Encourage the patient to take adequate fluid if diarrhea presents and treat dehydration.
- Provide antipyretic and pain-relieving medicine as ordered.
- Monitor temperature to identify signs of infection.
- Check vitals four hourly and record them.
- Provide isolation care and properly dispose of all gowns, masks, and gloves.
- Avoid the spread of infection and do not serve another patient with measles patient.
- Encourage the patient to sneeze and coughing with caution and pit in a bin.
- Encourage the patient to stay out of home for 8 days and explain the importance properly.
- Provide psychological care.
- Ensure adequate rest to overcome symptoms within a few days.
- Check any complications such as ear infection, eye infection, and inform the doctor.
- Give antibiotic exactly as the doctor ordered.
- Keep the patient in an adequately ventilated room but free from drafts and chilling to avoid complications of pneumonia.
- Administer vitamin-A supplements for malnourished children to avoid complications.
- Give health education about vaccination.
- Encourage the patient and family to vaccinated the baby as a scheduled time to active immunity against measles.
- Encourage pregnant women who never experienced measles to take one HNIG to avoid measles.
- Maintain good hand hygiene to prevent secondary infection.
- Clean eyelid with saline solution to remove secretion and give eye drops.
- Keep the environment cool to reduce itching.
- Relieve itching of the skin by tepid bath and soothing lotion.
- Use cool mist vaporizer, mouthwash, and tablets to keep mucous membranes moist.
- Teach, guide, and supervise the correct technique of giving a sponge bath for the comfort of the patient.
More questions related to this topic:
- Measles: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatments.
- Measles – Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- Is Measles a Disease or a Virus?
- Is the Measles Fatal?
- Can You Get the Measles More than Once?
- How Many People Have Died from the Measles?
- Measles Disease Definition.
- Measles Disease Symptoms.
- Measles Symptoms.
- Measles Disease Facts.
- Measles Disease Treatment.

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “[email protected]”


I need to thank you for this fantastic read!! I certainly enjoyed every bit of it. I’ve got you book marked to look at new stuff you post
Am happy To Be the One who het This information thanks a lot
Wc
GOOD JOB!
GOOD NURSE!
KEEP IT UP!
I’M PROUD TO BE A NURSE!!!