Definition of Shock:
Shock is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body is not getting enough blood flow. Many organs can be damaged as a result. Shock requires immediate treatment and can get worse very rapidly. As many 1 in 5 people who suffer shock will die from it.
Classification of Shock:
The following classifications are given below:
Primary shock:
This occur acting at the time of the accident or sudden illness.
Secondary shock:
This may not develop until several hours after the accident or sudden illness and is unusually very serious.
Another Classification:
Oligaemic shock:
This occurs when the tissues have been damaged and there is loss or blood or fluid from the circulation. It is very commonly present in the following circumstances-
- Fracture,
- Hemorrhage,
- Burns and scalds,
- After surgical operation,
- In severe vomiting and diarrheas.
What is Anaphylactic Shock?
Anaphylaxis can also be called anaphylactic shock. It is an allergic reaction that can be life- threatening. In most cases, anaphylaxis will mean you need to take a trip to the emergency room.
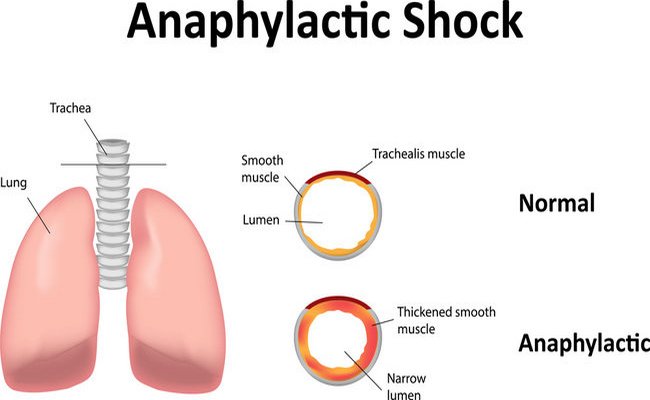
Causes of Anaphylactic Shock:
Common causes include foods such as peanuts, tree nuts (e.g. almonds, walnuts, cashews, and Brazil nuts), sesame, fish, shellfish, dairy products and eggs. Non-food causes include wasp or bee stings, natural latex (rubber), penicillin or any other drug or injection.
Clinical Features/Signs and Symptoms of Anaphylactic Shock:
The first signs of an anaphylactic reaction may look like typical allergy symptoms: a runny nose or a skin rash. But within about 30 minutes, more serious signs appear. There is usually more than one of these-
- Coughing; wheezing; and pain, itching, or tightness in your chest.
- Fainting, dizziness, confusion, or weakness.
- Hives; a rash; and itchy, swollen, or red skin.
- Runny or stuffy nose and sneezing.
- Shortness of breath or trouble breathing and rapid heartbeat.
- Swollen or itchy lips or tongue.
- Swollen or itchy throat, hoarse voice, trouble swallowing, tightness in your throat.
- Vomiting, diarrhea, or cramps.
- Weak pulse, paleness.

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”
