Respiratory Failure: Causes, Complication and Nursing Management
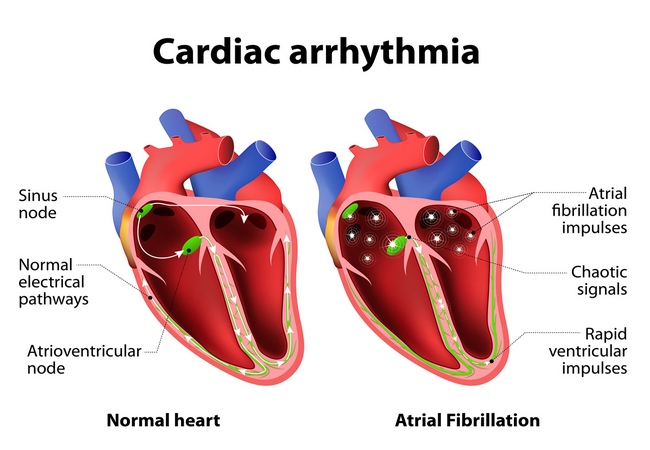
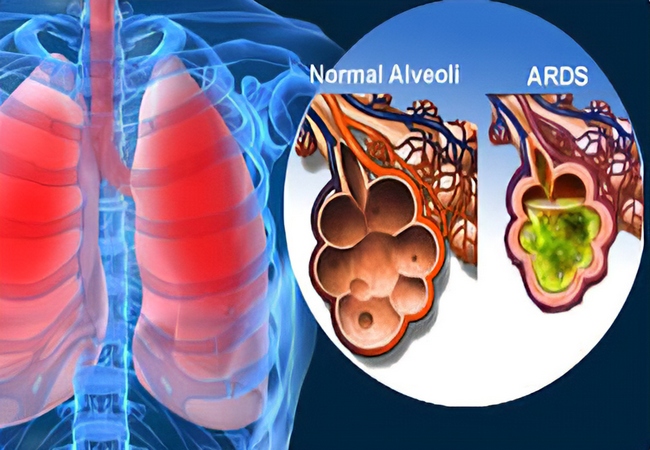
Definition of Respiratory Failure: The term respiratory failure is used when pulmonary gas exchange fails to maintain normal arterial Oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. Clinical Feature of Respiratory Failure: 1. Features of hypoxemia: Systemic Hypotension, Pulmonary HTN. Tachycardia, tachypnoea, polycythaemia Cerebral dysfunction ranging from confusion to coma. 2. Features of hypercapnoea: Confusion, Warm periphery, Flapping […]
Respiratory Failure: Causes, Complication and Nursing Management Read More »