All The Classification of Burns
What is Burn?
Damage to the skin or other body parts is caused by extreme heat, flame, and contact with heated objects or chemicals. Burn depth is general y categorized as a first, second, or third degree. The burn may be painful and may cause redness or peeling skin, blisters, swelling, and white or charred skin.
Classification of Burns Injury:
Burn is classified according to the different categories which are presented below:
It includes-
It is caused by conduction or convection. Example: hot liquid, fire or steam, etc.
It is caused by the passage of electrical current through the body. There is generally an exit and entrance wound.
It occurs when certain chemical compounds come in contact with the body. Example: Sulphuric acid, lye, hydrochloric acid, gasoline, etc.
It includes-
Branch of greatest destruction, tissue necrosis, immutable cell damage.
Harmed tissue, the area of less severe injury which possesses reversible damage and surrounds the zone of coagulation.
Pink, no cell depth, the area surrounding the zone of stasis that presents with inflammation but willfully any interventions or permanent damage.
It includes-
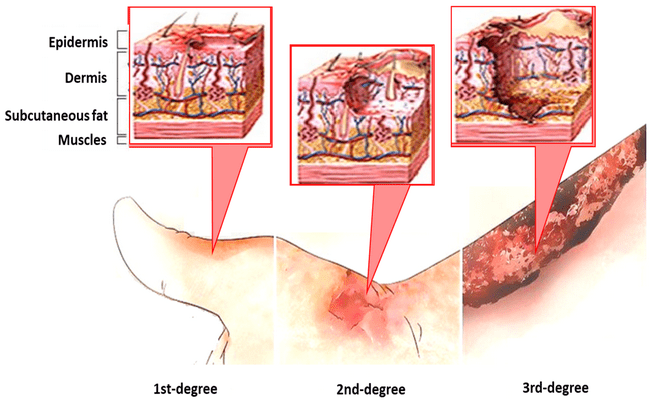
1. First Degree:
It includes only the outer layer of skin, the epidermis. Skin is usually red and very painful.
2. Second degree:
This type of burns involves the epidermis and part of the dermis layer of the skin. The second-degree burn site appears blistered, red, and maybe swollen and painful.
3. Third Degree:
All layers of the skin are destroyed. It extends into the subcutaneous tissues.
4. Fourth Degree:
It is the same as a third-degree but with damage to deeper structures such as tendons, joints, and bone.
It includes-
1. Superficial:
It involves only the outer epidermis, heals without scarring.
2. Superficial Partial-Thickness:
It involves the epidermis & the supper portion of the dermis, pain & blisters, heals with min to no scarring.
3. Deep- Partial-Thickness:
It completes the destruction of the epidermis & the majority of the dermis, blisters, edema; it may heal with hypertrophic scars & keloids.
4. Full-Thickness:
It completes the destruction of the epidermis & dermis along with partial damage of the subcutaneous fat layer. It requires grafts & susceptible to infection.
5. Sub-dermal:
It completes the destruction of the epidermis, dermis & subcutaneous tissue, which may involve muscle & bone. It often requires surgical intervention.
- What is meant by burns?
- Define burns.
- What are the classifications of burns?
- What are the types of burns?
- Explain different types of burns.
- Discuss different types of burns.
- Describe the classification of burns.

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”
