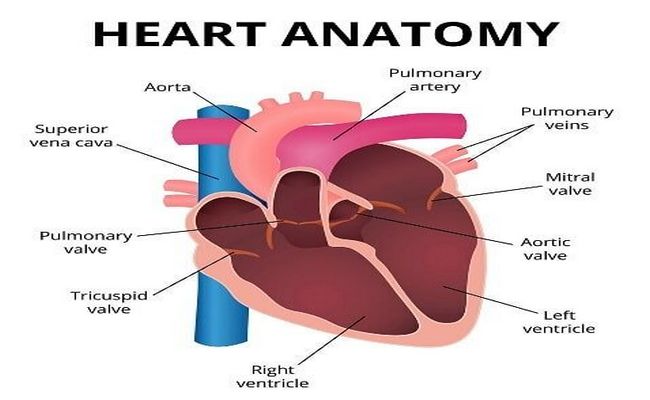
What are the Main Heart Chambers and Valves?
Chambers of the Heart:
The heart has four chambers. Those are listed below:
- Right atrium,
- Right ventricle,
- Left atrium,
- Left ventricle.
The two atria are separated from each other by a vertical septum is called the interventricular septum. The right atrium communicates with the right ventricle through the right atrioventricular orifice, which is guarded by three cusps. The left atrium communicates with the left ventricle through the atrioventricular orifice, which is guarded by two cusps.
The right atrium is the right upper chamber of the heart. It receives venous blood from the whole body through three veins:
Superior vena cava and inferior vena cava: Together these veins deliver blood from the body to the heart.
Coronary sinus, that returns blood from the walls of the heart itself. The right atrium pumps blood to the right ventricle through the right atrioventricular or tricuspid opening.
All the internal features of the right atrium have presented the below:
- The interior of the right atrium is divided into two continuous spaces: smooth-walled posterior part and rough-walled anterior part. Internally, this division is marked by the crista terminals, which is a smooth, muscular ridge. It corresponds to sulcus terminals externally.
- The rough anterior part presents musculi pectinate, which fans out from the crista terminals like the: teeth of the comb”.
- The interatrial septum that separates the right atrium from the left atrium, presents fossa ovalis. It is a depression just above the orifice of the inferior vena cava.
2. Right Ventricle:
The right ventricle is a triangular chamber that receives blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the lungs through the pulmonary trunk and pulmonary arteries.
It includes-
- The outflow tract of the right ventricle that leads to the pulmonary trunk is the conus arteriosus (Infundibulum). This area is smooth.
- Trabeculae carnae are irregular muscular ridges.
- Papillary muscles. The three papillary muscles are lying among the trabeculae carnage. These are- anterior, posterior, and septal.
3. Left Atrium:
The left atrium is a quadrangular chamber that is situated posteriorly. It receives oxygenated blood from the lungs through four pulmonary veins and pumps it to the left ventricle through the left atrioventricular orifice (mitral orifice).
4. Left Ventricle:
The left ventricle is a conical chamber. It is longer than the right ventricle and has the thickest layer of the myocardium.
It includes-
- Trabeculae care,
- Two papillary muscles- Anterior and posterior,
- Two orifices- left atrioventricular or mitral orifice and aortic orifice.
The valves of the heart include-
1. Atrioventricular valves: Right atrioventricular valve (tricuspid valve) and left atrioventricular valve (Bicuspid or mitral valve),
2. Semilunar valves: Aortic valve and pulmonary valve.
There are 4 (2 pairs) valves in the heart:
- A pair of atrioventricular valves- In between atria and ventricles.
- A pair of semilunar valves- At the opening of blood vessels arising from the ventricles, namely aorta and pulmonary artery.

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”
