Meningitis Definition:
It is a rare infection that affects the delicate membranes called meninges that covers the spinal cord and brain. You or your children can be affected by it. There are different types of meningitis disease including viral, bacterial, and fungal.
Among those, bacterial meningitis can be life-threatening that spreads between people in close contact with each other. Death can occur in as little as within a few hours. Most people recover from this type of disease. However, there are some permanent disabilities like hearing loss, brain damage, and learning disabilities that can result from the infection.
Sign and Symptoms of Meningitis:
All the clinical features are pointed out below:
1. Newborn Baby:
It includes-
- Vacant stare,
- Fever/hypothermia,
- Constant crying,
- Vomiting,
- Reluctant to feed,
- Poor tone and poor cry,
- Convulsion,
- Fontanelle may bulge,
- Neck rigidity absent,
- Kernig’s sign may present.
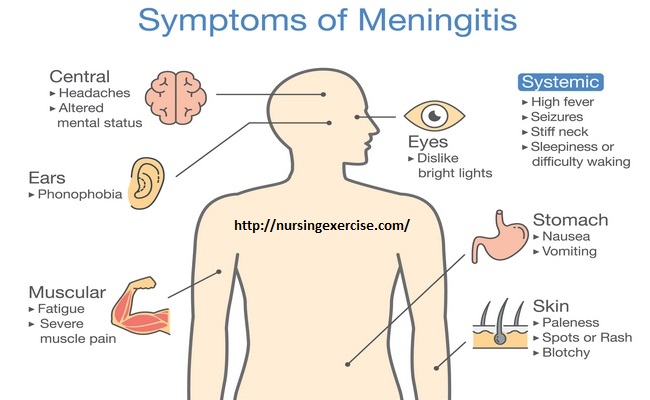
2. Older Children and Adult:
It includes-
- Fever with cold hands and feet,
- Severe headache,
- Vomiting,
- Drowsiness, difficulty to concentrate,
- Confusion and irritability,
- Neck stiffness/rigidity,
- Photophobia,
- Convulsion/seizure,
- Pale, mottled or blotchy skin, spots or rash,
- Muscle and joint pain.
Pathophysiology of Meningitis:

Diagnostic Test for Meningitis Disease:
There are different diagnostic tests for this type of disease infection. Those are listed in the following:
1. Specific Investigation:
It includes-
- CSF study (see the table below),
- Blood for cultural sensitivity test- may be positive,
- CT scan of the brain to exclude a mass lesion, eg. Cerebral abscess.
CSF Findings of Different Meningitis:
Points | Normal findings | Bacterial meningitis | Viral | Tubercular |
1. Color | Clear | Cloudy | clear | Spider web/fine clot |
2. Pressure | 50-180 mm of water | Increased | Normal | Increased |
3. Cell count | 0-4 (lymphocytes) | Polymorphs 1000-50000/cm | Lymphocytes 10-2000 | Lymphocytes 50-5000 |
4. Glucose | 40-80 mg/dl | Decreased | Normal | Decreased |
5. Protein | 20-40 mg/dl | Increased | Normal | Increased |
6. Chloride | 720-750 mg/dl | Decreased | Normal | Decreased |
2. Routine Investigation:
It includes-
- CBC- Neutrophilic leukocytosis (Increased WBC, Neutrophil),
- Urine for Routine Examination- Increased epithelial cells/ Pus cell numerous,
- Random Blood Sugar.
Early and Late Complications of Meningitis:
Complications of this type of disease can be severe. The greater the risk of seizures and permanent neurological damage of you or your child, the longer you or your child has the disease without treatment. All the possible complications of these kinds of disease have listed in the following:
1. Early Complication:
It includes-
- Increase intracranial pressure (ICP),
- Seizures,
- Cranial nerve palsies,
- hearing loss,
- vision loss,
- memory problems,
- arthritis,
- migraine headaches.
2. Late Complication:
It includes-
- Permanent brain damage,
- Hydrocephalus,
- Cerebral palsy,
- Mental retardation,
- Total blindness.
Author of This Article-
Shahinur Begum
Asst. Editor of Nursing Exercise
Dhaka, Bangladesh
Email: bshahinur1975@yahoo.com

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”
