What is Stomatitis Disease?
Stomatitis disease is an inflamed and sore inside of the cheeks, gums, tongue, lips, and palate. Stomatitis can severely affect speech; eating ability, nutrition, body image, sleep, and overall quality of life. Ulceration causes pain, bleeding, and infection. Stomatitis treatment includes oral hygiene, antiviral medication, topical or parental analgesia. Nurses play an important role in maintaining and restoring a healthy oral cavity through nursing interventions.
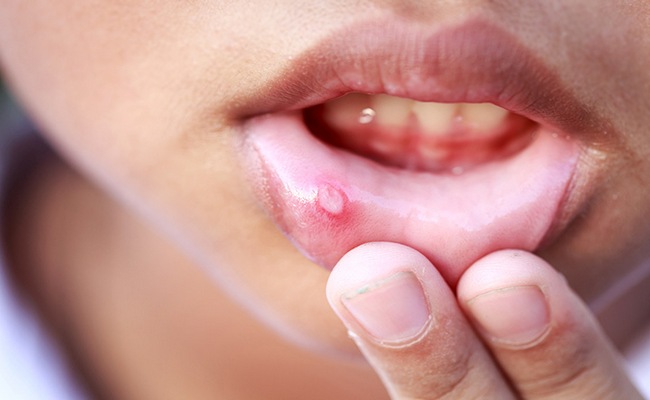
The patient will report less discomfort in her mouth while eating or drinking and mucous membranes will be free from harmful plaque. The nurse will help to prevent secondary infection throughout the hospital stay.
Definition of Stomatitis Disease:
Stomatitis refers to inflammation of the mucous membrane of the mouth including the inside of the cheeks, gums, tongue, lips, and palate.
Different Types of Stomatitis Disease:
There are three types of stomatitis, those are-
- Kanker Sore (Aphthous Stomatitis),
- Cold Sore (Fever Blisters),
- Herpes Stomatitis.
These are discussed below:
1. Kanker Sore (Aphthous Stomatitis):
Kanker Sore (Aphthous Stomatitis) is a single pill or a cluster of small pits or ulcers in the mouth. Usually canker sore appears on the cheeks, tongue, or inside the lip.
2. Cold Sore (Fever Blisters):
Cold Sore (Fever Blisters) is filled with fluid that usually appears on the lip or around the lips.
3. Herpes Stomatitis:
Herpes Stomatitis is a viral infection of the mouth that causes sores and ulcers. Usually in age children between six months to five years aged. Herpes simplex1 (HSV1) virus is the cause of infection.
Causes of Stomatitis Disease:
Various types of causes for stomatitis are mentioned below:
- Bacteria/Virus (Herpes Simplex type-1).
- Nutritional deficiency (Vitamin B12, Folic acid, Iron, or Zinc).
- Sudden weight loss.
- Food sensitivities to potatoes, citrus, fruits, strawberries, chocolate, eggs, cheese, or nuts.
- Inflammatory bowel disease.
- HIV/ AIDS.
- Weak immune system.
- Hormonal changes.
- Stress and lack of sleep.
- Use of certain medications such as Chemotherapy, Diuretics, Anticholinergics, Antihistamines and decongestants, Steroids, Antidepressants.
- Allergic reaction.
- Accidental injury.
- Sharp tooth surface, dental braces, or retainers.
- Tobacco or irritating foods or chemicals.
Sign and Symptoms of Stomatitis Disease:
There are different types of sign and symptoms for stomatitis disease are mentioned below:
- Blister over gums, palate, cheek, tongue, or lip,
- The difficulty of eating, drinking, and swallowing,
- Drooling, pain and swelling,
- Irritation,
- Fever,
- Red patches,
- Oral dysaesthesia,
- Burning mouth syndrome.
Test and Diagnosis for Stomatitis Disease:
Various ways of test and diagnosis system for stomatitis disease are given in the following:
- Bacterial or viral swabs culture,
- Biopsy,
- Patch tests,
- Blood test.
Treatment for Stomatitis Disease:
There are different types of treatment for stomatitis disease; those are mentioned below:
- Oral hygiene,
- Identify and treat the cause,
- Use antiviral drug acyclovir,
- Coating agents such as bismuth Salicylate, Sucralfate, or other Antacids,
- Topical Analgesics, such as Benzydamine Hydrochloride,
- In severe pain use Topical Anesthetics, such as Lidocaine viscous (might impair gag reflex for a short period),
- Oral or parenteral analgesics such as Tylenol or ibuprofen when not controlled by the above medication,
- Apply a paste of Triamcinolone,
- Water-soluble lubricants for mouth and lips,
- Rinse and expectorate after meals with Inj.Dexamethasone (0.5mg) / 5ml water.
- In nutritional deficiency is the cause of Stomatitis take folate (folic acid), vitamin B12.
Treatment of severe stomatitis sore may include-
- Aphthasol paste (Anti-inflammatory paste),
- Lidex gel,
- Peridex mouthwash.
Prevention of Stomatitis Disease:
Different types of prevention for stomatitis disease are given in the following:
- Wash hands frequently,
- Keep toys, brush clean and don’t share with others,
- Don’t share dishes, cups, or eating utensils,
- Don’t kiss the affected person.
Nursing Intervention for Stomatitis Disease:
There are various types of nursing interventions for stomatitis disease, those are mentioned below:
- Give cool, noncarbonated, non-acidic drinks, such as water, milkshakes, or diluted apple juice to the patient.
- Encourage the use of a straw to make swallowing easier.
- Provide a high in protein and vitamins containing diet to promote healing and new tissue growth.
- Serve frequent small meals or snacks spaced throughout the day to maintain fluid balance and nutrition.
- Offer cool, bland, easy-to-swallow foods such as frozen pops, ice cream, mashed potatoes, gelatine, or applesauce to the patient to avoid tissue trauma and pain.
- Encourage the client to suck on vitamin C or sugarless candy or chew sugarless gum to stimulate salivation.
- Encourage a fluid intake of at least 2500 ml/day unless contraindicated.
- Apply topical analgesia over the lesion 15 to 20 minutes before meals, or painted on each lesion immediately before mealtime.
- Give Acyclovir to the patient that fights the virus causing the infection.
- Give pain killer acetaminophen or ibuprofen for pain as order.
- Administer medications, which may include antifungal agents or topical or systemic analgesics.
- Give mouth care and gently brush teeth every day instruct and assist the client to perform oral hygiene using a soft bristle toothbrush or sponge-tipped swab.
- Discontinue flossing if it causes pain.
- Encourage the client to rinse mouth frequently with warm saline solution, baking soda, and water, or Chlorhexidine, Gluconate (Peridex) or mist oral cavity frequently using a spray bottle.
- Numbing medicine (Viscous Lidocaine) apply to a patient’s mouth to ease severe pain.
- Avoid the use of products that contain lemon and glycerine and mouthwashes containing alcohol.
- Lubricate the client’s lips frequently.
- If stomatitis is not severe, encourage the client to use artificial saliva to lubricate the oral mucous membrane.
- Make sure to get plenty of sleep and rests as much as possible.
- Encourage the client to chew on the ice during chemotherapy infusion, especially if receiving 5-fluorouracil.
- Avoid serve hot beverages, salty, spicy, and citrus-based foods and explain to the patient.
More questions related to this topic:
- Stomatitis: Types, Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment.
- Stomatitis | Definition and Patient Education.
- What is Stomatitis in Cats?
- Feline Stomatitis in Cats – Veterinary Dental Care for Cats.
- Vesicular Stomatitis In Horses.
- Stomatitis – Dental Disorders.
- Stomatitis Definition.
- Stomatitis Types.
- What is the Cause of Mouth Ulcers?
- Stomatitis Reasons.
- What are the Symptoms of Stomatitis?
- How to Cure Stomatitis?

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a “Senior Staff Nurse” at “Dinajpur Medical College Hospital”, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”

I ALSO LEARNT THAT APTOUS STOMATITIS IS COMMON BETWEEN THE AGES OF 8YRS TO 19YRS. PANCREATIC STOMATITIS WHICH IS CAUSED BY THE FUNGAL INFECTION IN THE MOUTH CALLED TRASH.IT NORMALLY OCCUR IN CHILDREN WHO HAS NOT BEING WELL BREASTFED.