Nursing Management of Tonsillitis Disease and Tonsil Medicine Name
What is Tonsillitis Disease?
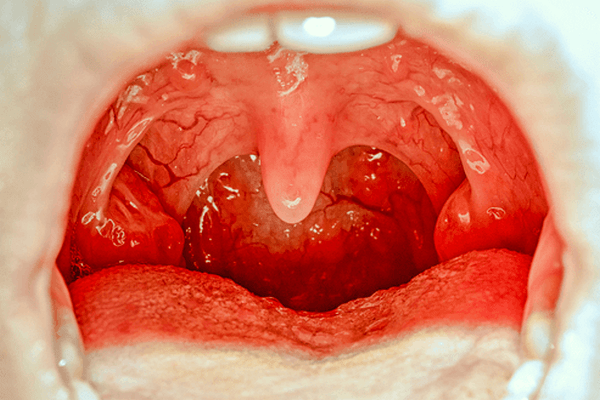
Tonsillitis disease can happen at any age and it is a common childhood infection. Tonsillitis disease is most often diagnosed in children from preschool age through their mid-teens. There are some common symptoms of tonsillitis disease are swollen tonsils, sore throat, and fever.
Nursing Management of Tonsillitis Disease:
- Antipyretics,
- Bed rest,
- Liquid or a soft diet,
- Analgesic,
- An analgesic lozenge in the early stage is helpful,
- Systematic antibiotics (penicillin) should be administrated parentally for 7 days,
- Isolation from other children to prevent the spread of infection,
- Hot saline gargle or gargles with aspirin in solution may be useful,
- Other antibiotics (erythromycin, cephalexin) can be served.
Management of chronic tonsillitis is done with tonsillectomy. It is indicated if medical treatment is unsuccessful and there is severe hypertrophy of tonsils. It should be advised in more than six significant attacks of tonsillitis in a year for two consecutive years and presence of the peritonsillar or retrotonsiliar abscess.
Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy are done under general anesthesia. After surgery-
- The child is placed in a side-lying position (tonsillectomy position).
- As bleeding is the main complication of tonsillectomy, this position facilitates drainage of any blood and secretions and prevents aspiration and swallowing.
- A child is closely observed in the post-operative period for swallowing movements of the throat.
- Repeated swallowing movement means that there is bleeding and the child is swallowing it.
- Pulse is recorded every fifteen minutes and a rising pulse rate is again a feature of bleeding. Falling blood pressure also indicates bleeding.
- When a child becomes conscious and if permitted by the anesthetist, he may be given cold fluids like fruit juices or cold drinks.
- Later on, soft foods are also started.
The below list presents the medicine name of tonsillitis disease.
- Zinacef,
- Suprax,
- Cepacol Dual Relief Sore Throat,
- Chloraseptic Sore Throat Lozenges,
- Benzocaine,
- Cefprozil,
- Cepacol Sore Throat,
- Aspirin/chlorpheniramine/phenylephrine,
- Bicillin L-A,
- Penicillin g benzathine,
- Trocaine,
- Cepacol Fizzlers,
- Cheracol Sore Throat,
- Assure Sore Throat,
- Cefditoren,
- Procaine penicillin,
- Laryngesic,
- Penicillin G Procaine,
- Amoxicillin,
- Spectracef,
- Wycillin,
- Azithromycin Dose Pack,
- Amoxil,
- Chloraseptic Sore Throat Spray,
- Zithromax,
- Cefuroxime,
- Cefdinir,
- Azithromycin,
- Clarithromycin,
- Penicillin VK,
- Benzocaine/menthol,
- Ceftin,
- Moxatag,
- Cefixime,
- Apo-Amoxi,
- Biaxin,
- Cefadroxil,
- Phenol,
- Zmax,
- Penicillin v potassium,
- Moxilin,
- Duricef,
- Cefpodoxime,
- Cefaclor,
- Cefzil.

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”
