What is Traction in Orthopedics?
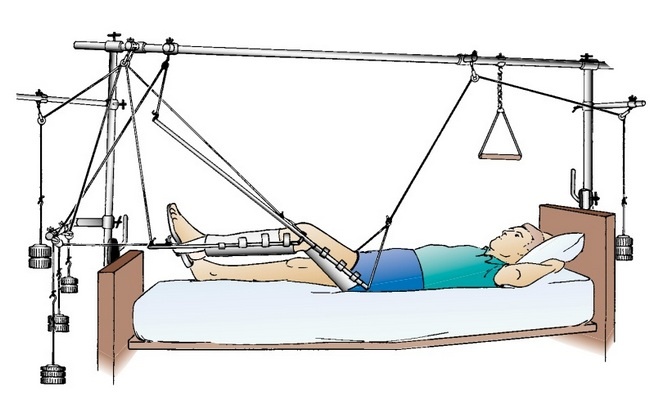
Principles of Traction in Orthopedics:
There are some key principles of traction which are mentioned below:
- In orthopedic, traction is a process of pulling structures of the musculoskeletal system to reduce and immobilize a fracture.
- Traction provides accurate bone alignment and also reduces muscle spasms.
- For traction to achieve its purpose, it requires counter traction, a force opposite to the mechanical pull. Counter-traction is usually supplied by the client’s own weight.
- To apply the force needed to overcome the natural force or pull of muscle groups, a system of ropes, pulleys, and weight is used.
All the purposes of traction have listed in the following:
- To reduce and immobilize a fracture,
- To retrieve the original length and alignment of an injured extremity,
- To lessen or eliminate muscle spasm,
- To prevent deformity,
- To give the patient freedom for “in-bed” activities,
- To reduce the pain.
Principles of effective traction are-
- Maintain proper body alignment,
- Apply the exact amount of weight prescribed,
- Ensure that the weights do not touch the floor and hang freely,
- Do not lift or remove the weights without a physician’s suggestion,
- Suspend splints and slings without interference,
- Ensure that the pulleys are not obstructed and that ropes in the pulleys move freely,
- Place notes in the ropes to prevent slipping,
- Check the ropes for fraying.
Different types of traction have discussed below:
It includes-
- A form of traction in which the pull is exerted in one plan,
- It may use either skin or skeletal traction,
- Buck’s extension traction is one of the examples of running skin traction.
Description:
- Uses additional weights to counterbalance the traction force and floats the extremity in the traction apparatus,
- Used with skin or skeletal traction,
- Used to conjectural fractures of the tibia, femur, or fibula,
- Despite changes in the patient’s position, the line of pull on the extremity remains fairly constant.
- Position the client in low Fowler’s on either the side of the back,
- From the thigh to the bed, maintain a 20-degree angle,
- Protect the skin from breakdown,
- If pins are used with skeletal traction, provide pin care,
- Clean the pin sites with sterile normal saline and hydrogen peroxide or Beta-dine as prescribed or per agency procedure.
3. Dunlop’s Traction:
Description:
Vertical traction maintains the forearm in proper alignment and horizontal traction to align fractures of the humerus.
Implementation:
- To the traction, a boot appliance is applied to attach.
- Weight is normally attached to a pulley; consent the weights to hang freely over the edge of the bed.
- No more than 8-10 pounds of weight should be applied.
- To provide traction, elevate the foot of the bed.
More questions related to this article:
- What do you mean by traction in orthopedics?
- What is traction?
- Define traction.
- What are the key principles of traction in orthopedics?
- What are the purposes of traction in orthopedics?
- Describe different types of traction in orthopedics?
- What are the principles of traction in physiotherapy?
- What type of traction is Buck’s traction?

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”
