Treatment and Nursing Management of Leukemia Disease
Definition of Leukemia Disease:
Leukemia are the disease in which abnormal proliferation of haemopoietic cells cause progressively increasing infiltration of the bone marrow and other tissues such as lymph node, liver & spleen. It is a disease of abnormal proliferation and maturation of bone marrow which interferes with the production of normal RBCs, WBCs and platelets.
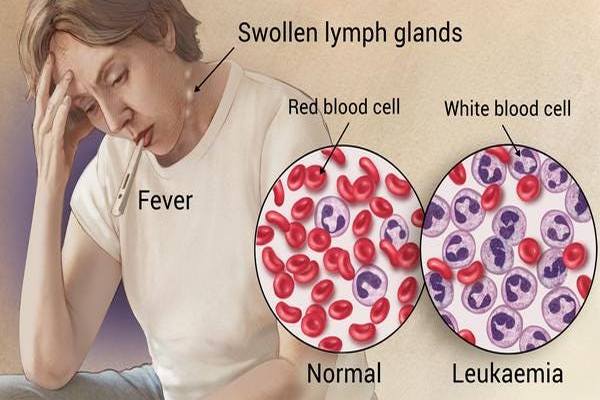
These are malignant disorders of the haemopoietic stem cell compartment, characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and/ or peripheral blood. That means, malignant neoplasm of haemopoietic cell is called Leukaemia.
Treatment of Acute Leukemia Disease:
1. Specific Rx: Chemotherapy: Only 2 phases
Phages 1: (Remission induction):
- Daunorubicin (IV),
- Cytarabine (IV),
- Etoposide (IV and oral),
- Tioguanine (oral).
Phase 2: (Remission consolidation):
- Cytarabine (IV),
- Amsacrine (IV),
- Mitoxantrone (IV).
2. Supportive Rx:
- Correction of anemia: Fresh blood transfusion, packed cell transfusion.
- Correction of bleeding.
- Broad spectrum antibiotic.
- Maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance.
- Monitoring of renal and hepatic function.
- Psychological support.
- Alternative chemotherapy -Hydrourea and mercaptopurine.
- Curative Rx: Bone marrow transplantation.
Nursing Management or Intervention of Leukemia:
1. Providing emotional support to the parent to reduce parental anxiety. Encouraging the parents to express their feeling and answering their questions honestly.
2. Necessary information and instructions to be given to the parents and family members to avail support services, community resources and religious help to adjust with the stress situation.
3. Preventing infections and hemorrhage. The following measures to be followed:
- Maintaining aseptic technique, hygienic measures, general cleanliness, good hand-washing practices, restriction of visitors and taking precautions during any invasive procedures.
- Administering antibiotics; as prescribed. Oral and IV route to be used. Intramuscular injection should be best avoided.
- Precautions to be taken during blood transfusion.
- Avoiding injury. Soft toothbrush can be used for dental care. Soft jelly to be applied for dry lips. Nonirritating mouth wash to be used, no alcohol to be used. Breaking of skin and mucous membrane to be avoided.
- Monitoring vital signs, urinary output, hydration level, signs of infections, bleeding or other complications.
4. Relieving pain by rest, comfort, minimizing exertion, promoting relaxation and diversion and administering prescribed analgesics.
5. Maintaining normal body temperature by tepid sponge in high feve4 airy environment, adequate fluid intake, avoiding overclothing and hot environment, administering antipyretics and other prescribed drugs.
6. Recording vital signs 4 hourly. Avoid use of rectal thermometer.
7. Promoting adequate nutritional intake with high nutritious diet with small frequent feed.
8. Avoiding high salty food, when steroids are given.
9. Antiemetics to be given to prevent vomiting.
10. Diet should be attractive and tasty to promote intake of more amount.
11. Explaining about the change of body image, especially in case of alopecia due to chemotherapy.
More questions related to this article:
- What do you mean by leukemia?
- What is leukemia?
- Define leukemia.
- State the treatment of acute leukemia.
- Describe the nursing management of leukemia
- Write down the nursing management of a child with anemia.

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”
