Definition of Cardiac Arrhythmia:
Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregular heartbeat- the heart may beat too fast (tachycardia), too slowly (bradycardia), too early (premature contraction), or irregularly (fibrillation. Arrhythmias occur when the electrical signals to the heart that coordinate heartbeats are not working properly.
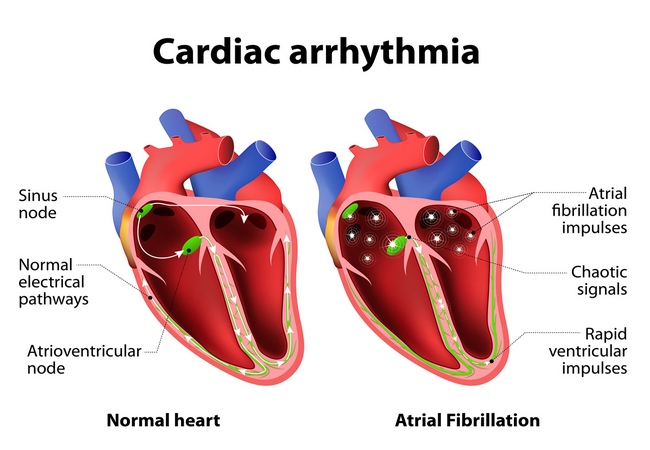
Types of Cardiac Arrhythmia:
- Tachycardia: A fast heart rhythm with a rate of more than 100 beats per minute.
- Bradycardia: A slow heart rhythm with a rate below 60 beats per minute.
- Supraventricular arrhythmias: Arrhythmias that begin in the atria (the heart’s upper chambers). “Supra” means above; “ventricular” refers to the lower chambers of the heart, or ventricles.
- Ventricular arrhythmias: Arrhythmias that begin in the ventricles (the heart’s lower chambers).
- Bradyarrhythmias: Slow heart rhythms that may be caused by disease in the heart’s conduction system, such as the sinoatrial (SA) node, atrio-ventricular (AV) node or HIS- Purkinje network.
Causes of Cardiac Arrhythmia:
A number of factors can cause the heart to work incorrectly, they include:
- Alcohol abuse,
- Diabetes,
- Drug abuse,
- Excessive coffee consumption,
- Heart disease,
- Hypertension (high blood pressure),
- Hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid gland),
- Mental stress,
- Scarring of the heart, often the result of a heart attack,
- Smoking,
- Some dietary supplements,
- Some herbal treatments,
- Some medications.
A healthy person will hardly ever suffer from long-term arrhythmia unless they have an external trigger, such as drug abuse or an electric shock.
Arrhythmia can develop if a condition has changed the structure of the heart, for instance:
- Coronary artery disease arteries in the heart narrow, often resulting in a heart attack
- Cardiomyopathy – disease of the myocardium (heart muscle)
- Valvular heart diseases – if the heart valves narrow or leak, the heart muscle can stretch and thicken.
Sign and Symptoms of Cardiac Arrhythmia:
Noticeable arrhythmia symptoms may include:
- A fluttering in chest,
- A racing heartbeat (tachycardia),
- A slow heartbeat (bradycardia),
- Chest pain,
- Shortness of breath,
- Lightheadedness or dizziness,
- Sweating Fainting (syncope) or near fainting.
Symptoms of Cardiac Arrhythmia:
Some patients may have no symptoms at all, but a doctor might detect an arrhythmia during a routine examination.
1. Symptoms of tachycardia:
- Breathlessness,
- Dizziness,
- Syncope (fainting, or nearly fainting),
- Fluttering in the chest,
- Lightheadedness,
- Sudden weakness.
2. Symptoms of bradycardia:
- Angina (chest pain),
- Trouble concentrating,
- Confusion,
- Difficulties when exercising,
- Dizziness Fatigue (tiredness),
- Lightheadedness,
- Palpitations,
- Shortness of breath,
- Syncope (fainting or nearly fainting).
3. Symptoms of atrial fibrillation:
- Angina (chest pain),
- Breathlessness,
- Dizziness,
- Palpitations,
- Syncope (fainting, or nearly fainting),
- Weakness.

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”
