Definition of Nutritional Anaemia or Anemia:
The qualitative and quantitative deficiency of red blood cell is called anaemia. Anaemia due to mineral and vitamin deficiency is called nutritional anaemia. Nutritional anaemia is moderate to serve public health problem in Bangladesh.
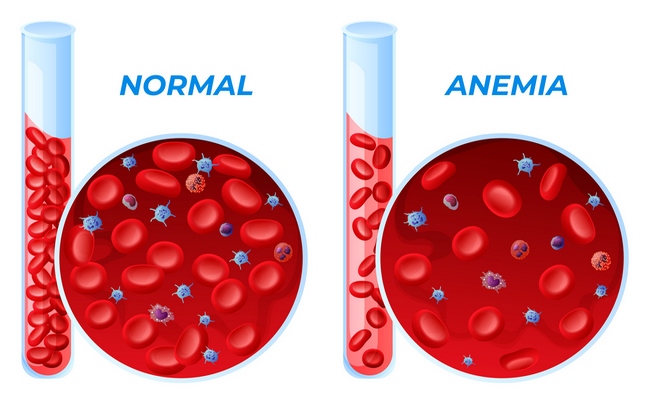
Anaemia refers to a state in which the level of haemoglobin in the blood is below the normal range appropriate for age and sex. Anaemia means that the blood does not contain enough haemoglobin-the substance that makes blood red, people sometimes call anaemia ‘weak blood’ or ‘thin blood’ or ‘pale blood’. When there is not enough haemoglobin, it is more difficult to get oxygen to the cell.
List of Common Name of Nutritional Anaemia or Anemia:
Common nutritional anaemia includes-
- Iron deficiency anaemia,
- Folic acid deficiency anaemia. (Megaloblastic anaemia),
- Vitamin B12 deficiency anaemia. (Megaloblasic anaemia).
Common Causes of Anaemia or Anemia in Bangladesh:
All the common causes of anaemia in Bangladesh have pointed out in the below:
- Lack of iron and folate in diet,
- Frequent pregnancy,
- Hook worm infestation,
- Peptic ulcer disease,
- Excessive menstrual bleeding,
- Carcinoma of stomach, colon etc.,
- Chronic renal failure,
- Haematological malignancy,
- Aplastic anaemia,
- Congenital haemolytic anaemia,
- Anaemia of chronic disease.
Signs and Symptoms of Anaemia or Anemia:
Clinical Features of Anaemia or Anemia:
Different Symptoms of Anaemia or Anemia:
It includes the following-
- Fatigue,
- Tiredness,
- Effort intolerance,
- Effort dyspnoca,
- Palpitations,
- Headache,
- Faintness,
- Giddiness,
- Pounding in the ear,
- Effort angina.
Common Signs of Anaemia or Anemia:
It includes the following-
- Pallor,
- Tachycardia,
- Koilonychia-Iron deficiency anaemia,
- Jaundice-Haemolytic anaemia,
- Haemolytic facies-Haemolytic anaemia,
- Bleeding manifestation- Aplastic anaemia, anaemia due to bone marrow infiltration such as leukaemia,
- Temperature-Aplastic anaemia, anaemia due to bone marrow infiltration such as leukaemia,
- Lymphadenopathy-Anaemia due to leukaemia, rymphoma etc.,
- Systolic flow murmur,
- High cardiac output state,
- Features ofcongestive cardiac failure,
- Leg ulcer-sickle cell anaemia.
Prevention of Iron Deficiency Anaemia or Anemia:
1. Iron and folic acid supplementation. If haemoglobin is between 10– 12 g/dl, dosage for-
- Mothers: 1 tablet (60mg of elemental iron +0.5 mg folic acid) daily for 2 to 3 months or longer depending upon the progress,
- Children (6 months to 1 and 2 years): tablet (20mg of elemental iron +0.1 mg of folic acid) daily.
2. Iron fortification, e.g. iron fortified salt.
3. Others: Changing dietary habits, control of parasites, and nutrition education.
Sites for Checking Anaemia or Look for Anaemia:
It includes-
- Lower palpebral conjunctiva,
- Dorsal (upper) surface of tongue,
- Palm (palmar crease) of the hand,
- Sole of the feet,
- Nail beds,
- Buccal mucous membrane,
- Whole body skin.
Intervention or Prevention of Anaemia or Anemia:
1. Iron and folic acid supplementation:
Dosage:
Mothers:
- 1 tab of iron & folic containing 60 mg of elemental iron (180 mg of ferrous sulfate),
- 5 mg of folic acid should be given daily up to 2-3 months.
Children:
- 1 tab of iron and folic acid containing 20 mg of elemental iron (60 mg of ferrous sulphate) mg of folic acid should be given daily.
Iron fortification:
- Iron fortification with salt by adding ferric ortho-phosphate or ferrous sulphate with Na bis- sulphate.
- Iron fortification has many advantages over implementation as salt is a universally consumed dietary item.
3. Long term measures:
- Changing dietary habits,
- Control of parasites,
- Nutrition education.
More questions related to this article:
- What do you mean by anaemia?
- What do you mean by anemia?
- List the name of common nutritional anaemia.
- What are the common causes of anaemia in Bangladesh?
- What are the sign and symptoms of anaemia?
- What are the clinical features of anaemia?
- How will you prevent of iron deficiency anaemia?
- Write down the sites for checking anaemia.
- How will you prevent nutritional anaemia in the community?
- What are the interventions of anaemia?
- What are the prevention of anaemia?

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”
