Early Signs and Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
What is Tubal Pregnancy or Ectopic Pregnancy?
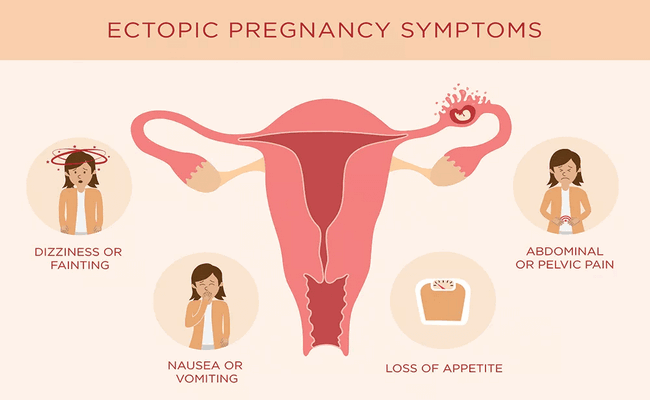
What are the Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy?
Various clinical features of ectopic pregnancy have mentioned in the following:
1. Per abdominal examination:
It includes-
- Abdomen intense and tender and tenderness more in the lower abdomen,
- Shifting dullness may be elicited,
- The gut may be distended.
2. Per vaginal examination:
It includes-
- Usually not done due to fear of precipitating more bleeding and extreme tenderness,
- Vaginal mucosa blanched white,
- No mass usually felt through the cervix,
- Extreme tenderness on palpation of the fornix or movement of the cervix.
3. A short period of amenorrhea,
4. Severe lancinating pain in one iliac fossa or the hypogastrium immediately followed by profound collapse,
5. Slight, sanguineous, or dark-colored vaginal bleeding,
6. Feeling of nausea, vomiting, and dyspnea,
7. There may be anemia, fever (2% of cases), and signs of shock.
All the diagnosis ways of acute ruptured ectopic pregnancy have pointed out below:
It includes-
- Exhibits abdominal or pelvic tenderness during palpation,
- Tenderness in patients with EP may be generalized (45%), located bilaterally in the lower quadrants (25%), or located unilaterally in a lower quadrant (30%),
- Rebound tenderness may or may not be present,
- A palpable adnexal mass or mass in the cul-de-sac is reported in approximately 40% of cases; absence of a palpable mass does not rule out EP,
- Additional signs include shoulder pain (15%) and low-grade fever (Less than 10%).
2. P/V Examination:
It should not be done due to tenderness.
3. Lab Investigation:
Blood:
It includes-
- TC, DC (Neutrophilic leukocytosis),
- Hb% below normal,
- ESR raised,
- Blood grouping and Rh typing- should be done for management beta-HCG.
Urine Specific Gravity (USG):
It includes-
- TVS (Transvaginal sonography is the choice)- can detect an EP greater than 2cm,
- USG can show,
- Empty uterus,
- Cystic or sold adnexal masses,
- Dilated and thick-walled fallopian tubes,
- Free echogenic fluid in the pelvis; hematosalpinx,
- The extrauterine gestational sac contains a yolk sac, with or without an embryo.
More questions related to this article:
- What is the definition of ectopic pregnancy?
- What do you mean by ectopic pregnancy?
- What is the clinical feature of ectopic pregnancy?
- What are the sign and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy?
- What are the first signs of an ectopic pregnancy?
- When do ectopic pregnancy symptoms start?
- What’s ectopic pregnancy pain like?
- Can you have symptoms of ectopic pregnancy?
- What are the first signs of tubal pregnancy?
- What are the early signs of an ectopic pregnancy?
- How to diagnose ectopic pregnancy?
- How to prevent ectopic pregnancy?
- What are the early signs of tubal pregnancy?

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a “Senior Staff Nurse” at “Dinajpur Medical College Hospital”, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”
