What is Heart Failure?
Heart failure disease also called congestive. Heart failure is a condition in which the heart fails to pump enough blood to the rest of the body. As a result, the main body or vital organs and other tissue do not receive enough oxygen and nutrient to function properly.
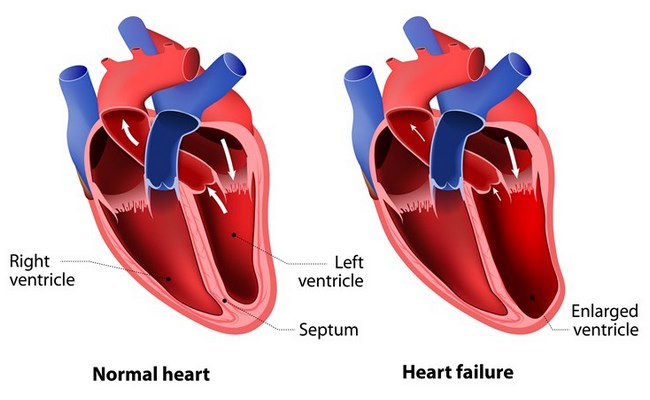
Types of Heart Failure Disease:
There are two types of heart failure. Those are discussed below:
1. Left-Sided Heart Failure Disease:
The left ventricle loses its ability to contract or relax normally. The heart cannot pump with enough force to push enough blood into circulation or the heart cannot properly fill with blood during the resting period between each beat.
2. Right Side Heart Failure Disease:
Right-sided heart failure occurs as a result of left-sided failure. When the left ventricle fails to pump, blood transferred back to the right ventricle through the lungs, ultimately damaging the right-sided heart.
Causes of Heart Failure Disease:
There are various causes of heart failure. Those are in the below:
- Coronary heart disease,
- Congenital heart disease,
- Heart attack,
- Cardiomyopathy,
- Hypertension,
- Valvular heart disease,
- Atrial fibrillation ( heart rhythm disturbance),
- Anemia,
- Pulmonary hypertension,
- Myocarditis,
- Heart Arrhythmias,
- DM,
- HIV,
- Hyperthyroidism or Hypothyroidism,
- Smoking,
- Obesity,
- Endocrine disorder,
- Fluid overload.
Sign and Symptoms of Heart Failure Disease or Heart Failure Symptoms:
The main sign and symptoms of heart failure are in the below-
- Shortness of breath,
- Frequent coughing or wheezing with white or pink blood-tinged phlegm,
- Fatigue & weakness,
- Swollen feet, ankles & leg,
- Abdominal swelling and pain,
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat,
- Decrease ability to exercise,
- Dizziness or fainting,
- Need to urinate at night,
- Swelling of the liver,
- Neck vein distension.
Test and Diagnosis of Heart Failure Disease:
The main tests and diagnosis of heart failure are below:
- BNP,
- Chest X-Ray,
- ECG,
- Electrocardiogram,
- Stress testing,
- Cardiac CT scan or MRI,
- Coronary angiogram.
Management of Heart Failure Disease or Heart Failure Disease Management or Heart Failure Guidelines:
There are two types of management of heart failure. Those are described in the below-
1. Treatment:
- ACE Inhibitors (to decrease afterload and cardiac hypertrophy) such as Captopril, Enalapril.
- Angiotensin II receptor inhibitors (Decrease cardiac hypertrophy and apoptosis) such as Losartan, Valsartan.
- Beta-Blockers (slow heart rate and improves cardiac output also reduce cardiac remodeling) such as Metoprolol, Bisoprolol.
- Diuretics (Decrease fluid overload) such as Furosemide, Bumetanide.
- Aldosterone Antagonists (decrease fluid overload) such as spironolactone.
- Inotropes (Dopamine, Dobutamine, Digoxin) improve heart pumping function which increases cardiac output slows heart rate to reduces the workload of hearts, and controls atrial fibrillation if present.
- Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet (Aspirin, Heparin, Warfarin).
2. Surgery:
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) helps to improve blood flow to the damaged or weakened heart muscle.
- Heart valve repair or replacement.
- Implantable cardioverter – defibrillators (ICDs). Its monitor’s heart rhythm. If the heart starts beating at a dangerous rhythm or stop. ICD tries to pace the heart or shock it back into a normal rhythm.
- Pacemaker
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) or biventricular pacing.
- Intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP).
- Left ventricular assist device.
- Heart transplantation.
A complication of Heart Failure Disease:
There are different types of complications for heart failure. Those are in the following-
- Hepatomegaly,
- Splenomegaly,
- Pleural effusion,
- Kidney damage or failure,
- Cardiogenic shock,
- Arrhythmia,
- Left ventricular thrombus and embolism,
- Death.
Nursing Intervention of Heart Failure Disease:
Those are various types of nursing intervention for heart failure which are mentioned in the following:
- Maintain semi fowlers’ position.
- Check vitals sign and record it.
- Give oxygen therapy according to saturation and keep spO2 ˃90%.
- Open intravenous line.
- Auscultate heart and lung sounds.
- Monitor oxygen saturation and ABG.
- Monitor results of laboratory and diagnostic tests.
- Indwelling urinary catheter and evaluate urine output.
- ECG is done within 10 minutes.
- Administer medication as indicated.
- Encourage periods of rest and assist with all activities.
- Establish a rapport relationship with the patient.
- Monitor intake output chart hourly.
- Monitor weight daily.
- Auscultate breath sounds every 2 hours.
- Provide a low sodium diet and keep fluid restriction.
- Monitor for distended neck veins and ascites.
- Encourage the use of incentive spirometry 4th.
- Assist with the activity of daily living.
- Provide a calm and quiet environment.
- Provide pt and family with opportunities to discuss their concerns.
More questions related to this topic:
- Congestive Heart Failure Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment.
- Congestive Heart Failure: Types, Causes, & Treatment.
- Congestive Heart Failure: Symptoms and Stages.
- Definition of Heart Failure Disease or Heart Attack Disease.
- What is Diastolic Heart Failure?
- Congestive Heart Failure Causes.
- What is the Cause of Heart Failure?
- What is the Most Common Cause of Left-Sided Heart Failure?
- Heart Failure Causes.
- What are the Symptoms of Congestive Heart Failure?

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a “Senior Staff Nurse” at “Dinajpur Medical College Hospital”, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”

Very,very educative