Hypertension Disease Definition:
Hypertension disease is known as high blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated when the 140/90mmhg or higher is called high blood pressure or hypertension.
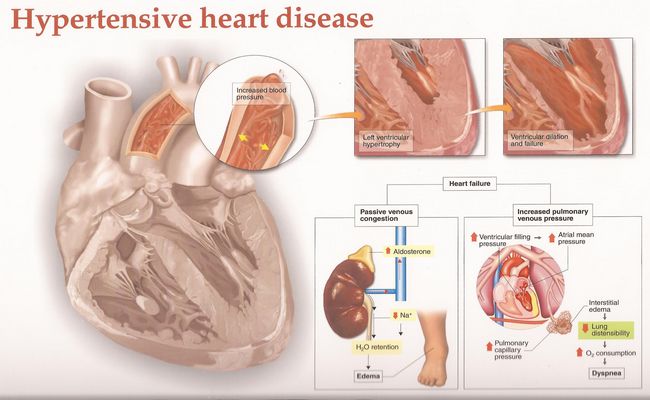
High Blood Pressure Dangers: Hypertension’s Effects
High blood pressure is diagnosed when one or both (systolic and diastolic) of these numbers is too high. Stage or categorized of blood pressure are the following:
Blood Pressure | Range |
Normal | Less than 120-80mmhg |
Prehypertension | 120-80mmhg to 139-89mmhg |
Stage-1 Hypertension | 140-90mmhg to 159-99 mmHg |
Stage-2 Hypertension | 160-100mmhg or higher |
Severe Hypertension | 180-110mmhg or higher |
Blood Pressure:
Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing up against the walls of blood vessels (Artery).the normal range of blood pressure 120/80mmhg.
Causes and Risk Factors of Hypertension Disease:
The main causes and risk factors of hypertension are below:
- Age,
- Genetic,
- Lack of exercise,
- Obesity,
- Stress and depression,
- Vitamin D deficiency,
- Smoking,
- Drug abuse and alcoholism,
- Cushing syndrome,
- Diabetes,
- Sedentary lifestyle,
- Intake of extra salt,
- Insufficient calcium, magnesium, and potassium intake,
- Chronic kidney disease,
- Adrenal and thyroid problems,
- Adrenal gland tumors,
- Thyroid problems,
- Certain medications such as birth control pills, cough, and cold remedies and over-the-counter pain relievers( NSAIDs),
- Obstructive sleep apnea.
Sign and Symptoms of Hypertension Disease:
Various symptoms of hypertension are the following:
- Severe headache,
- Fatigue or confusion,
- Blurred vision,
- Lightheadedness,
- Vertigo,
- Tinnitus,
- Fainting,
- Irregular heartbeat,
- Blood in the urine.
Diagnosis of Hypertension Disease:
Different diagnosis ways for hypertension are in the following:
- Manual checking of blood pressure by a sphygmomanometer,
- Family history,
- Cause and Risk factors.
Management of Hypertension Disease or Hypertension Disease Management:
There are two ways to control high blood pressure, which are below:
- Lifestyle modification,
- Medication.
1. Lifestyle Modification:
- Maintain normal weight ( weight loss),
- Take a healthy diet,
- Avoid extra salt,
- Quit smoking and alcoholism,
- Regular physical exercise,
- Avoid stress and depression,
- Control of blood sugar,
- Take potassium, calcium, and magnesium-rich diet.
2. Medication:
- ACE Inhibitors (Captopril, Enalapril, Perindopril, Quinapril). an ACE inhibitor is particularly.
- Useful if heart failure and diabetes present.
- Beta-blockers (Acebutolol, Atenolol, Bisoprolol, Propranolol, Timolol). Slowing the heart rate and reducing the force of the heart.
- Calcium channel blockers (Amlodipine, DIltiazem, Felodipine, Nifedipine, Verapamil). Relaxing blood vessels and control blood pressure.
- Diuretics (Bendroflumethiazide, Chlortalidone, Cyclopenthiazide and Indapamide). Reducing the extra fluid in blood and reduce blood pressure.
These medications can be used alone or combined to control blood pressure.
Prevention for Hypertension Disease or Hypertension Treatment:
There are different ways to prevention from hypertension which are the below:
- Control of normal body weight (e.g. body mass index 20 -25 kg/m2.
- Reduce intake of dietary sodium.
- Quit alcoholism and drug abuse.
- Engage in regular activity and perform daily physical exercise.
- Avoid stress and anxiety.
A complication for Hypertension Disease:
Various complication of hypertension are the following:
- Heart attack or stroke,
- Aneurysm,
- Weakened and narrowed blood vessels of the kidney,
- Heart failure,
- Thickened narrowed or torn blood vessels of eyes ( Blindness),
- Metabolic syndrome.
Nursing Intervention for Hypertension Disease:
Different nursing intervention for hypertension are the following:
- Monitor and measure blood pressure in both hands, using a cuff and proper techniques four hourly and compare with normal range and previous parameter of the patient.
- Check the quality of central and peripheral pulses.
- Auscultation of breath and heart sounds and observe skin color, moisture, temperature, and capillary refill time.
- Timely administer medication as indicated and do not administer two antihypertensive medicines at the same time.
- Monitor response of antihypertensive medication.
- Ensure bed rest and maintain restrictions on activities.
- Assist patient in self-care activities as needed.
- Provide a calm and quiet environment and reduce stress.
- Encourage the patient to express feeling and explain the patient’s condition from time to time.
- Provide low calorie, salt-restricted, and potassium, calcium, magnesium-rich diet, and explain the need for such type of diet.
- Minimize interruption and environmental stimuli.
- Provide analgesic and sedative drugs as ordered.
- Encourage patient to avoid constipation and ensure intake of fiber diet.
- Maintain fluid intake output carefully.
- Encourage and discuss the importance of controlling weight.
- Encourage the patient to establish an individual exercise program incorporating aerobic exercise.
- Monitor electrolytes and creatinine as indicated.
- Encourage the patient to quit alcohol and illicit drug use.
- Monitor sign symptoms of hypertension complications such as headache, dizziness, fainting, nausea, and vomiting.
More questions related to this topic:
- Hypertensive Heart Disease: Types, Symptoms & Diagnosis.
- Hypertension: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments.
- High Blood Pressure and Hypertensive Heart Disease.
- Hypertensive Heart Disease: Overview.
- What is Hypertensive Heart Disease?
- What is Hypertension Disease?
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Information
- What are the Dangers of High Blood Pressure?
- Can a Person Die from High Blood Pressure?
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension).

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”

what is it?i just understand that it is the good information about HTN…and how u get this ……..you know me details please maria