What is Pharyngitis Disease?
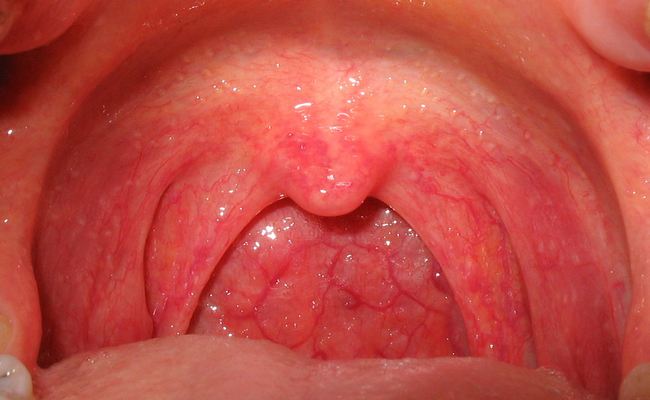
Most of the cases are caused by a viral infection. Strep throat, a bacterial infection is a reason in about 10% of adults and 25% of children. Rare causes include other bacteria i.e. fungus, gonorrhea, irritants such as smoke, allergies, and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Specific testing is not recommended in people who have clear symptoms of a viral infection such as the cold. Else a throat swab or a rapid antigen detection test (RAPD) is recommended. The other conditions that can produce the same symptoms include thyroiditis, epiglottitis, retropharyngeal abscess, and occasionally heart disease.
Types of Pharyngitis Disease:
There are three types of pharyngitis. Those are explained below:
1. Non-exudative Pharyngitis:
It does not produce fluids like pus. This type of pharyngitis disease is the most common which is generally caused by viruses.
2. Exudative Pharyngitis:
It produces a body fluid like pus. This usually suggests a bacterial cause.
3. Ulcerative Pharyngitis:
Ulcerative pharyngitis disease which is mainly caused by bacteria is infrequently seen but is considered to be a medical emergency.
There are two types of clinical features of pharyngitis. One is bacterial Pharyngitis and another one is viral pharyngitis.
Bacterial Pharyngitis:
It includes-
- Erythema,
- Bilateral tonsillar hypertrophy,
- Vomiting,
- Dysphagia due to a sore throat,
- Whitish exudate,
- A headache,
- Abdominal discomfort,
- Fever.
It includes-
- Tenderness of cervical lymph glands,
- Nonexudative erythema of pharynx,
- Anorexia,
- A cough,
- Nasal obstruction,
- Fever,
- Malaise,
- Hoarseness of voice,
- Nasal discharge.
Some major symptoms of pharyngitis are listed below:
- A runny nose,
- A cough,
- A headache,
- Hoarse voice.
Complications of pharyngitis have pointed out in the following:
- Mastoiditis,
- Otitis media,
- Peritonsillar abscess (quinsy),
- Mesenteric adenitis,
- Acute glomerulonephritis,
- Chronic ulcer in the throat,
- Sinusitis,
- Meningitis,
- Rheumatic fever.
There some key nursing management for pharyngitis which is presented below:
- Warm saline gargles (in older children),
- Analgesics,
- Antitussive,
- Antipyretics,
- Steam inhalation,
- Extra fluid intake,
- Liquid or soil diet,
- Oral hygiene,
- Nasal decongestant and anti-allergic may be needed for some children.
- Streptococcal pharyngitis should be treated with antibiotics (penicillin, amoxicillin, erythromycin, and cephalosporin) for 10-15 days with bed rest.
More questions related to this article:
- What do you mean by pharyngitis?
- What are the clinical features of pharyngitis?
- What are the types of pharyngitis?
- Describe the classification of pharyngitis.
- What are the symptoms of pharyngitis?
- What are the complications of pharyngitis?
- Describe the nursing management for pharyngitis.

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”
