Definitions of Cell Membrane:
All living cells and many of the tiny organelles are bounded by thin, tough, and elastic limiting membranes called the cell membrane. It acts as a selective barrier that separates the interior of a cell from its surroundings or outside environment. This outer boundary or selective barrier of the cell is also called the plasma membranes.
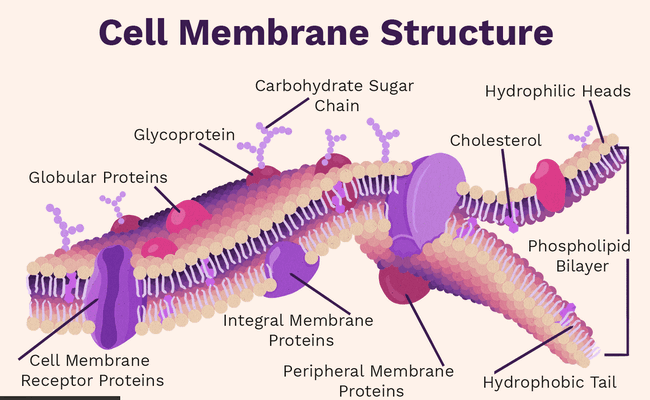
The fluid mosaic model describes the cell membrane as a tapestry of several types of molecules or components including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates—that give the membrane a fluid character. The ‘Fluid’ part explains how some parts of the membranes can move around freely if they are not attached to other parts of the cell. The ‘mosaic’ part represents the ‘patchwork’ of proteins that are found in the Phospholipid Bilayer.
They are attached to lipids (glycolipids) and to proteins (glycoproteins) that extend from the outward-facing surface of the membrane that is constantly moving. This movement assists the cell membranes to keep their role as a barrier between the inside and outside of the cell environments.
All the compositions of the membrane have pointed out the below with their percentage:
- Protein: 55%,
- Lipid: 42%,
- Phospholipid: 25%,
- Cholesterol: 13%,
- Other lipids: 4%,
- Carbohydrates: 3%.
Main Functions of Cell Membrane:
All the functions of the membrane have listed in the following:
- It helps to maintain the shape and size of the cell.
- Separate the intracellular components from the extracellular environment.
- It separates and retains one cell’s cytoplasm from another neighboring cell (act as a boundary).
- Proteins like glycoprotein, which are used for cell recognition and act as receptors and antigens.
- Phospholipid Bilayer creates a partially permeable membrane, which allows only certain substances to diffuse through the membrane.
- Cholesterol – maintains the fluidity of the cell surface membrane.
- Endocytosis: Membrane transports large molecules (or even whole cells) by engulfing them.
- Exocytosis: Membrane removes or secretes substances such as hormones or enzymes.
- It participates in the process of antibody.
- It removes or secretes substances such as hormones or enzymes.

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”
