Definition of Deep Vein Thrombosis:
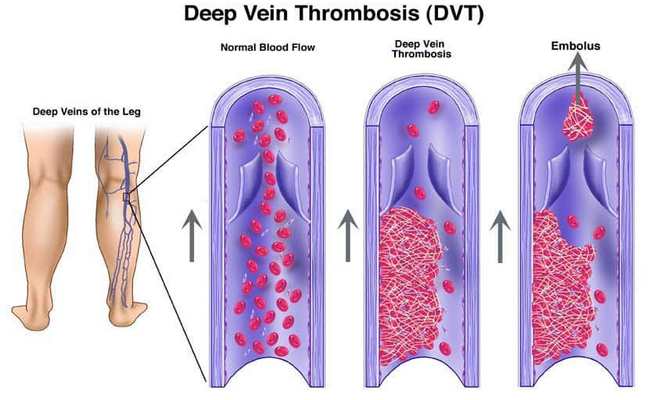
Deep vein thrombosis or DVT is a blood clot that forms in a deep vein inside the body. DVT usually occurs in a deep leg vein that runs through the muscle of the calf and the thigh. Blood clots form when blood thickness and clumps together.
Sign and Symptoms of Deep-Vein Thrombosis (DVT):
There are different sign and symptoms of DVT, those are in the following:
- Edema,
- Swelling of the leg,
- Distension of surface vein,
- Pain or tenderness,
- Warmth in the skin,
- Redness or discoloration,
- Leg fatigue,
- Calf pain on dorsiflexion of the foot (Homans sign).
Causes of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT):
Different causes of DVT are mentioned in the below:
- Immobility:
- Bed Ridden or Paralysis,
- Prolonged travel or sitting,
- Hospitalization,
- Fracture of legs or pelvis,
- Recent pelvic or knee surgery.
- Obesity,
- Pregnancy,
- Venous stasis,
- Hypercoagulability
- Birth control pill or hormone replacement therapy,
- Smoking,
- Genetic predisposition (Family history),
- Cancer,
- Congestive Heart Failure,
- Coronary heart disease,
- Age more than 60 years,
- Pace maker catheter,
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
Patho Physiology:
Blood cells contain platelets and protein known as clotting factors. When a blood vessel is cut and damaged, the platelets and clotting factors protein form a solid clot that acts as a plug to stop the wound bleeding. These are normal processes for blood clotting when blood vessel bleeds or damaged. But the blood clots form when blood vessel not damaged and restricts the blood flow, it’s called Deep-vein thrombosis and can lead a life threatening condition.
Diagnosis and Test for Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT):
Various diagnosis and test for DVT are in mentioned in the following:
- USG,
- Blood Test- D-Dimer, CBC,
- Vanography,
- CT or MRI Scans.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment:
There are different treatments for DVT; which are in the below:
- Anticoagulant:
- Warfarin,
- Heparin.
Heparin:
- Standard (Unfracted) Heparin- can be given as Intravenous injection),
- Low molecular weight Heparin (LMWH) -can be given as subcutaneous.
- Clot blusters- (Streptokinase, Urokinase),
- Direct Xa inhibitors -Apixaban(Eliquis), Edoxaban (Savaysa) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto),
- Direct Thrombin Inhibitor-Dabigatran (Pradaxa ),
- Filters (Inferior venucava filters),
- Compress stockings,
- Thrombectomy,
- Exercise.
Complications of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT):
There are different complication of DVT, those are mentioned in the below:
- Pulmonary embolism,
- Postphlebitic syndrome.
Nursing Intervention for Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT):
Various nursing intervention for DVT are in the following:
- Assess for and reports sign and symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis.
- Keep the affected leg elevated and comfortable position.
- Keep the head up of bed.
- Immobilize the patient and initiate bed rest to reduce risk of clot mobilization.
- Administer anticoagulants as ordered to reduce the risk of additional clotting.
- Carefully calculate heparin dose.
- Use infusion pump to administer intravenous heparin.
- Do not mix the heparinized solution with other medications.
- Discourage positions that compromise blood flow.
- Administer analgesics (Morphine) as ordered to manage pain.
- Apply warm compress to affected leg using a 2-hour-on, 2-hour-off schedule around the clock.
- Provide elastic compression stocking.
- Administer oxygen as ordered in order to maintain tissue perfusion.
- Check and monitor any sign of bleeding.
- Check any sign of complication (Pulmonary embolism).
- Obtain lab orders to monitor APTT, PT and INR.
- Ensure intake of vitamin-k rich food including green, leafy vegetable.
- Instruct patient to carefully brushing teeth to avoid bleeding.
- Instruct patient to keep nasal mucosa hydrate and moist.
- Ensure a minimum intravenous fluid intake of 2500ml per day for proper hydration unless contraindicated to prevent increase blood viscosity.
- Provide adequate knowledge to patient pertaining to warfarin therapy.
- Check any sign of excessive bleeding complication of warfarin therapy.
- Be aware of the signs of signs of excessive bleeding, such as frequent and bilateral epitasis, hematuria (blood in the urine) and deep tissue bruising (purpura).
- Advise the patient to take care when brushing teeth in order to reduce risk of bleeding gums.
- Discuss with patient the need to change method of contraception, if applicable (as oral contraceptives increase DVT risk).

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”

Great info to share
My symptoms started at the age of 47. My fingers on my left hand were stiff and were difficult to move. People noticed that my walk was not normal. I was often asked did I hurt. I noticed nothing different about my walk. It was difficult getting up from` a chair and getting out of a car. I was diagnosed a year later ,it was the onset of tremors starting in my right hand that caused my other symptoms to be recognized as Parkinson’s.. I am now 59. With the new herbal medicine i purchase from totalcureherbsfoundation .c om was my only way to get rid of my PD,the herbal formula effectively reverse my condition and alleviate all symptoms.
I have been having a frequent problem with my body’s vein which has been very visible for a couple of months. I was really getting scared about this problem. I am now on various medicine for this disease. This a very well-written article for those who know very little about Deep Vein Thrombosis.