Difference Between Meiosis and Mitosis
What is Cell Division?
Cell division is a basic process in all living organisms involving the separation of the genetic material into two or more daughter cells. Thus, cell division is an essentially biological process involved in the growth, replenishment (repair), and reproduction of various organisms. It is part of the organism’s cell cycle.
What is Mitosis?
Mitosis is the process of cell division by which the cytoplasm and nucleus of the cells are divided equally to give rise to two genetically identical daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes. The main purpose of mitosis is for growth and to replace worn-out cells.
Meiosis is a special type of cell division that produces four haploid cells from a diploid parent cell containing half the original amount of genetic information. Meiosis produces our sex cells or gametes– Sperm in males, eggs in females.
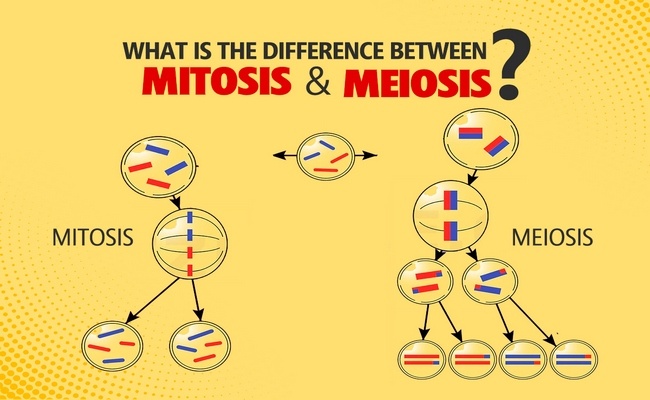
Difference between Meiosis and Mitosis:
SL No. | Differential factors | Mitosis | Meiosis |
01 | Site | Occur in somatic cell ( body cell) | Occur only in sex cell (gametes) |
02 | Formation of daughter cell | The Diploid number of Identical two daughter cell those contain the same number of chromosomes. | The Haploid number of four daughter cells contains one-half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. |
03 | Pairing | Not occur | Occur |
04 | Type | No, any type | Two types occur · Meiosis -I · Meiosis – II |
05 | Phase | One phase | Two different phase |
06 | Number of division | One and equational division | Two and reductional division |
07 | Subdivision | No subdivision present in the prophase | Subdivision present in prophase e.g.
|
08 | Cytokinesis (the division of the cytoplasm) | Occurs at the end of telophase | Happens at the end of telophase I and telophase II. |
09 | Chromosome | Not visible | Visible |
10 | Tetrad Formation | Does not occur | Occur In prophase |
11 | Chiasmata and crossing over | No formation of chiasmata and crossing over not occur | Formation of chaismata and crossing over occurs (prophase I) |
12 | Genetic materials | No exchange of genetic materials | Random exchange of genetic material occurs |
13 | Chromosome number | Remains the same | Reduced by half |
14 | Synapsis | No | Yes – from bivalents |
15 | Duration | Short | Long |
16 | Role in the animal body | Produce a cell for growth and repair | Produce gametes and assure genetic diversity in sexual reproduction |
17 | Cell cycle | Occurs throughout the life cycle | In humans, completes after sexual maturity |

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”
