Definition of Mumps Disease:
Mumps is an acute infectious and communicable disease characterized by fever, tenderness and localized swelling of one or more of the salivary gland, usually the parotid and occasionally the sublingual or sub maxillary glands. It is an acute infectious disease caused by a specific virus affecting the glandular and nervous tissues.
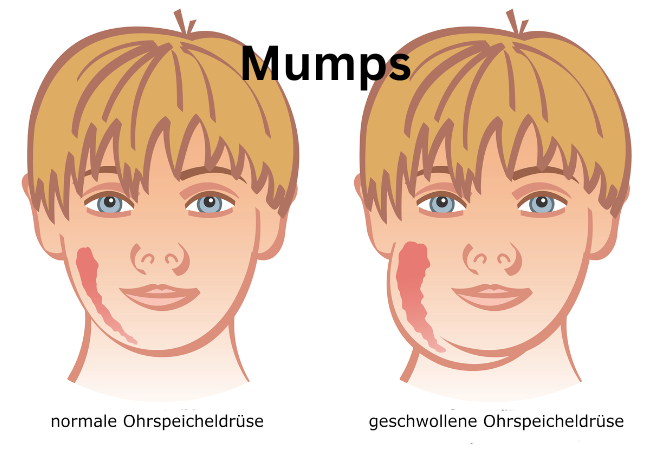
Epidemiological Feature of Mumps Disease:
1. Occurrence: The disease is worldwide in occurrence.
2. Ecological triad:
Agent factors:
- Agent: Myxovirus parotiditis.
- Source of infection: Both clinical and sub-clinical cases.
- Period of communicability: 4-6 days before the onset of symptoms and a week or more thereafter.
- Secondary attack rate: Very high
Host factors:
- Age and sex: Mumps is the most frequent cause of parotitis in the age group of 5-15 years. However the infection can occur at any age.
- Immunity: One attack is supposed to confer lifelong immunity.
3. Environmental factors: Peak incidence in winter and spring. Epidemics are often associated with overcrowding.
4. Mode of transmission:
- Person to person by respiratory droplet.
- By direct contact with items that have been contaminated.
5. Incubation period: Usually 12-24 days.
6. Organs involved in mumps:
- Salivary glands,
- Extra salivary glands: Testis, pancreas, ovaries, CNS, prostate.
7. Organ involved in mumps are:
- Salivary gland,
- Extra salivary glands-testis, Pancreas, ovaries, CNS, Prostate.
Clinical Features or Sign and Symptoms of Mumps Disease:
Mumps is manifested as generalized viral infection. Approximately one-third cases are asymptomatic.
The initial features are –
- Fever,
- Headache,
- Nausea,
- Malaise,
- Anorexia,
- Sore throat.
- Earaches and pain behind the ear on chewing and swallowing are diagnostic features found usually within 24 hours of onset.
- Tender edematous swelling of the parotid glands is found within 1 to 3 days.
- The enlargement of gland displaced the car lobe upwards and outwards.
- The sub-maxillary and sublingual glands may also be involved later.
Treatment of Mumps Disease:
There is no specific treatment for mumps. The symptomatic management includes –
- Antipyretics and analgesic to treat fever and pain.
- Steroids may be administered to relief pain and swelling in case of orchitis.
- Bed rest and local support to be provided for the child with orchitis.
- Warm saline mouth wash and liquid diet is needed in difficulty of chewing.
- The child should be kept isolated.
- Early detection of complications and prompt management to be done to prevent long-term sequelae.
Complications of Mumps Disease:
Most mumps complications involve inflammation and swelling in some part of the body, such as:
1. Testicles:
This condition, khown as orchitis, causes one or both testicles to swell in males who’ve reached puberty. Orchitis is painful, but it rarely leads to sterility – the inability to father a child.
2. Pancreas:
The signs and symptoms of this condition, known as pancreatitis, include pain in the upper abdomen, nausea and vomiting.
3. Ovaries and breasts:
Females who’ve reached puberty may have inflammation in the ovaries (oophoritis) or breasts (mastitis). Fertility is rarely affected.
4. Brain:
A viral infection, such as mumps, can lead to inflammation of the brain (encephalitis). Encephalitis can lead to neurological problems and become life-threatening.
5. Membranes and fluid around the brain and spinal cord. This condition, known as meningitis, can occur if the mumps virus spreads through your bloodstream to infect your central nervous system.
Other complications:
1. Hearing loss:
In rare cases, mumps can cause hearing loss, usually permanent, in one or both ears.
2. Miscarriage:
Although it isn’t proved, contracting mumps while you’re pregnant, especially early on, may lead to miscarriage.
More questions related to this article:
- What do you mean by mumps?
- What is mumps?
- Define mumps.
- Write down the epidemiological features of mumps.
- Write down the clinical features of mumps.
- What are the sign and symptoms of mumps?
- What is the treatment of mumps?
- Write down the complications of mumps?

Maria Khatun Mona is a Founder and Editor of Nursing Exercise Blog. She is a Nursing and Midwifery Expert. Currently she is working as a Registered Nurse at Evercare Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. She has great passion in writing different articles on Nursing and Midwifery. Mail her at “maria.mona023@gmail.com”
